AI Platform Security Architecture: Multi-Tenant RAG & Agent Patterns
AI security conversations usually start with prompt injection and OWASP-style threats-but enterprise buyers also want to know how your platform prevents cross-tenant access, locks down RAG pipelines, and keeps AI agents from touching the wrong database rows. This guide covers the platform controls I implement on Next.js AI platform engagements so engineering teams can satisfy enterprise security requirements without revealing proprietary code.
Modern AI platforms aren’t just a single app and a model-they’re an ecosystem: frontends, orchestration layers, agents, RAG pipelines, vector stores, background workers, and third-party APIs stitched together. Every surface can leak data, be abused, or drift out of compliance if it isn’t designed with security in mind. This guide is the high-level security architecture for that ecosystem. If you want deep dives on specific layers, pair this with:
- AI Agent Architecture - agent orchestration and tool safety
- LLM Security Guide - model-specific threats and mitigations
- Penetration Testing AI Platforms - how we test real systems
- Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture - tenant isolation, RLS, data boundaries
- RAG Architecture Guide - retrieval, semantic search, data-plane risks
Scope: Platform architecture security (database, API, RAG, agent orchestration, observability). For model-level controls-including detailed prompt injection defenses and OWASP mappings-see the LLM Security Guide.
Pillar: This is the pillar page for AI security on the site. The LLM Security Guide and Penetration Testing AI Platforms posts are spoke deep dives that link back here.
What you’ll learn
- Threat modeling for multi-tenant AI SaaS
- RLS-first data isolation patterns for Supabase/Postgres/Neon
- RAG security pipeline design (pre/post validation, vector DB isolation)
- AI agent hardening (tool registry, MCP servers, RBAC, logging)
- Platform integration security (Next.js routes, Edge runtime, third-party APIs)
- Operational security + monitoring for AI workloads
- Testing strategies focused on platform integration and adversarial tenants
Need a readiness check before an enterprise launch? Schedule a penetration test and we’ll combine automated scanning with manual red teaming tailored to AI platforms. For LLM-specific threats, see the LLM Security Guide; for multi-tenant schemas, see the multi-tenant SaaS security patterns.
Related Deep-Dives
- AI Agent Architecture - How agents and tools are orchestrated safely.
- LLM Security Guide - Model-specific threats and mitigations.
- Penetration Testing AI Platforms - How real AI systems are tested.
- Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture - Isolation, RLS, and shared-data boundary design.
- RAG Architecture Guide - Retrieval, semantic search, and secure indexing.
- AI Platform Development Stack - Recommended stack for AI platforms.
Threat model: platform attack surface
Every security review starts by mapping how tenants, services, and LLM layers interact. The recurring findings:
| Threat | Vector | Platform impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-tenant data leakage | Missing RLS, unsanitized vector search, shared caches | Compliance failure, legal risk |
| Prompt injection + tool abuse | Malicious prompts, poisoned documents, open-ended tools | Unauthorized commands, key leaks |
| Auth bypass | Weak session validation, missing middleware, JWT tampering | Tenant impersonation |
| RAG retrieval gaps | Filters applied after similarity search, stale metadata | Sensitive docs exposed |
| Agent orchestration flaws | Tools registered without RBAC, missing logging | No audit trail, silent privilege escalation |
| Observability blind spots | No tenant IDs in logs, missing tool telemetry | Incidents can’t be investigated |
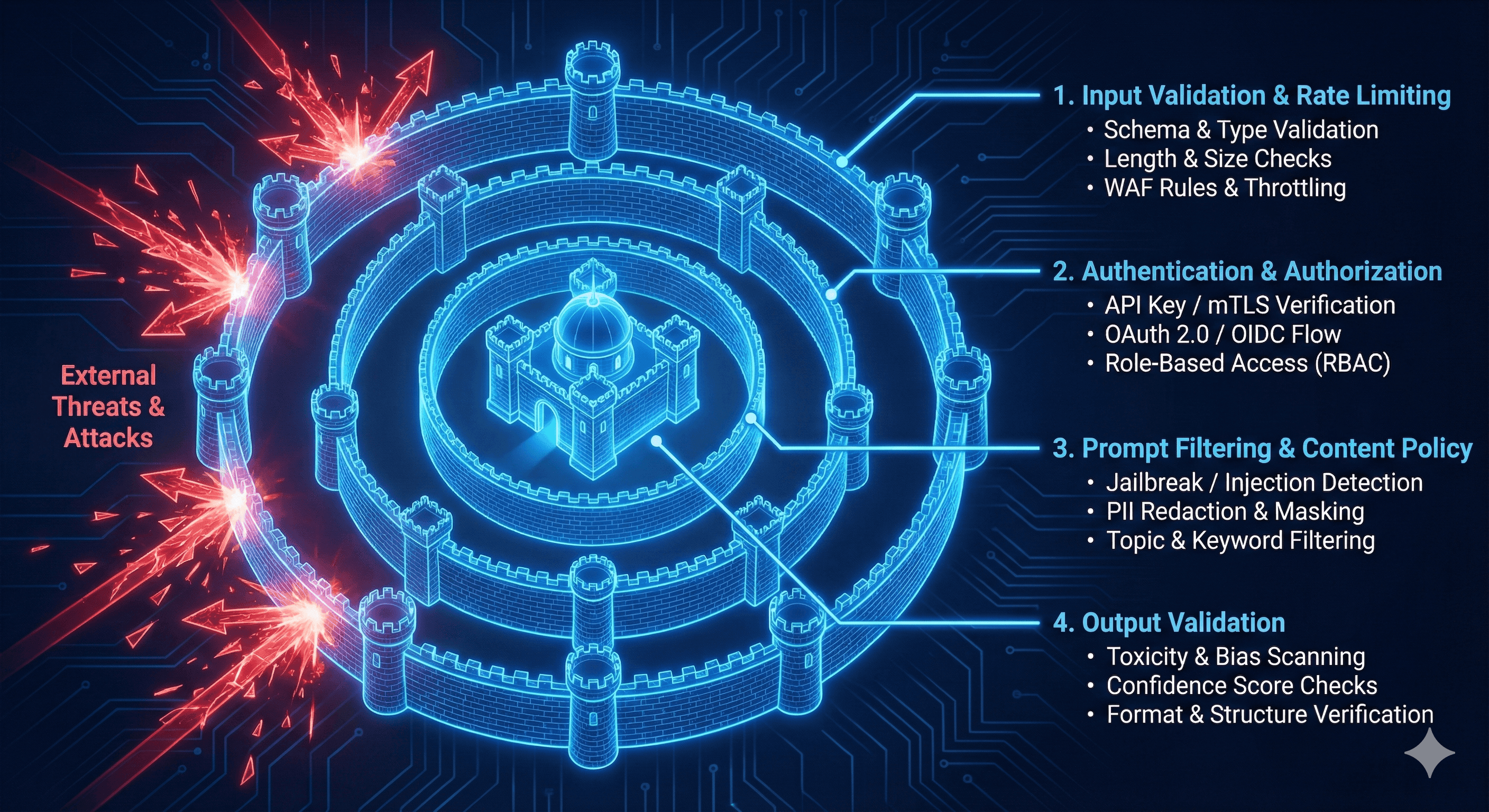
Defense-in-depth security layers for AI applications showing threat model and security boundaries.
Defend the stack in layers-database, API/middleware, RAG, agent orchestration, and ops. If one layer misfires, the next must stop the leak.
AI Platform Security Architecture
Key security boundaries:
- Authentication/Authorization (teal): Session validation, tenant verification
- Data layer (red): RLS policies, vector namespace isolation, row-level security
- Observability (yellow): Tenant-tagged logs, audit trails, incident response
Security maturity model
| Stage | Characteristics | Priority controls |
|---|---|---|
| MVP | Few tenants, limited automation | Basic RLS, per-tenant auth, logging with tenant IDs, manual incident response |
| Growth | Dozens of tenants, audits starting | Automated onboarding, RBAC, rate limiting, dashboards, quarterly pen tests |
| Enterprise-ready | Procurement reviews, AI assistants, multi-region | AI guardrails, zero-trust networking, disaster recovery drills, vendor risk management |
Use this table as a roadmap. Early-stage teams focus on RLS + auth basics; as you grow, layer observability, automated testing, and AI-specific controls. For schema and tenancy economics see the multi-tenant SaaS architecture guide.
Multi-tenant isolation: RLS-first design
RLS is your last line of defense. Application code will miss a tenant_id filter at some point-RLS catches it.
Core principles
- Database-level enforcement - Every tenant-owned table requires RLS policies that filter by tenant context
- Session-based tenant context - Set tenant ID at the connection/session level before any queries execute
- Composite indexing - Structure indexes to support efficient tenant-scoped queries
- Fail-closed architecture - Missing or invalid tenant context must result in 403 errors, never default behavior
Critical implementation areas
Middleware & API routes
- Extract tenant ID from authenticated session
- Inject tenant context into request headers
- Set database session variables before queries
- Validate tenant membership for every request
Connection pooling - Properly manage tenant context across connection reuse to prevent cross-tenant leakage
Service roles - Restrict service role usage to backend jobs that explicitly impersonate tenants
Serverless & Edge - Handle tenant context in stateless environments (Vercel Edge, Cloudflare Workers)
Cache isolation - Namespace all caches by tenant ID to prevent data leakage
Testing strategy
- Concurrency tests simulating simultaneous multi-tenant access
- Missing-context tests verifying fail-closed behavior
- SQL injection attempts targeting tenant_id overrides
- Background job tenant context validation
Need implementation details? Row-level security patterns, schema design, middleware setup, and testing frameworks require deep customization for your stack. See the comprehensive Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture Guide for detailed RLS implementation patterns, or contact us for hands-on implementation support.
RAG security: four guardrails for retrieval
RAG pipelines blend vector search, keyword filters, and LLM prompts. Each stage needs tenant awareness.
1. Pre-retrieval validation
- Input sanitization - Enforce length limits, strip dangerous content, block injection patterns
- Tenant membership verification - Validate requesting user belongs to referenced tenant
- Query classification - Route queries appropriately (RAG vs FAQ vs knowledge base)
2. Tenant-filtered vector search
- Apply tenant filters before similarity search, not after
- Use metadata filters (pgvector WHERE clauses) or namespaced indexes (Pinecone/Qdrant)
- Isolate embedding caches per tenant
- Limit result sets to prevent token/cost abuse
3. Post-retrieval verification
- Validate chunk metadata matches requesting tenant before LLM injection
- Log security events for any cross-tenant retrieval attempts
- Fail closed with generic errors rather than leaking partial data
- Track retrieval patterns for anomaly detection
4. Output validation & citation enforcement
- Verify citations reference only approved chunks
- Run DLP filters for sensitive data patterns (SSNs, API keys, credit cards)
- Detect cross-tenant mentions in responses
- Enforce content policy compliance
Attack pattern: Cross-tenant data comparison
Attackers craft prompts like “Show Acme vs. Beta metrics” hoping tenant filters applied after vector search will leak data into context. Defend with:
- Pre-retrieval tenant filtering
- Post-retrieval chunk validation
- Output filtering for cross-tenant mentions
- Comprehensive logging for security analysis
Implementation considerations
- Structure API routes with middleware that injects tenant context before retrieval
- Use edge middleware to block unauthenticated requests early
- Return structured JSON responses to prevent XSS from retrieved content
- Monitor retrieval latency and cost per tenant
Deep dive: For complete RAG architecture including hybrid search, chunking strategies, reranking, and detailed security patterns, see the RAG Architecture Guide. For adversarial testing, explore AI Security Consulting and Penetration Testing services.
AI agent security: registry, RBAC, and state
Agents combine LLM planning with tool execution-great for automation, terrifying for auditors unless you show how tools are governed.
Tool registry architecture
- Catalog management - Store tool metadata (capabilities, schemas, costs, tenant scope)
- Permission mapping - Define role-based access to tools per tenant
- Session filtering - Expose only authorized tools based on tenant + role context
- Execution gateway - Centralized validation, quota enforcement, and logging before tool invocation
RBAC & tenant isolation
- Separate sessions per tenant (no global tool access)
- Multi-agent RBAC (planner/worker/verifier with distinct permissions)
- Comprehensive logging of authorized and denied attempts
- Anomaly detection for repeated denial patterns (injection indicators)
Argument validation & state management
- Schema validation for all tool arguments (types, ranges, enums)
- Tenant ID verification for resource references
- Restricted free-form text inputs to prevent injection
- Encrypted, tenant-scoped state storage with TTLs
MCP servers in production
- HTTPS with authentication (OAuth2, API keys)
- Filtered manifests based on user roles
- Per-tenant namespacing or dynamic manifest generation
- Rich instrumentation (tool, tenant, user, duration, status)
Implementation guide: For complete agent architecture patterns including MCP integration, tool orchestration, and multi-agent systems, see the AI Agent Architecture Guide. For hands-on implementation, AI Platform Development includes tool registries, RBAC, and logging from day one.
Prompt injection & LLM-layer defenses (in brief)
Prompt injection sits one layer above platform controls. Keep a minimal summary here and link to the dedicated guide:
- Treat prompt injection like SQL injection: sanitize inputs, isolate instructions, filter outputs, and test continuously.
- Use platform telemetry (tenant IDs, tool usage) to triage injection attempts.
- For a full breakdown-including six defense layers, code snippets, and testing harnesses-see the LLM Security Guide.
Platform integration & Edge security
Next.js API routes
- Wrap every
/app/api/*handler with auth middleware. Verify tenant context and role before touching business logic. - Use
headers.get('x-tenant-id')rather than trusting request bodies. - Return structured errors with correlation IDs so incidents can be traced.
Middleware & Edge runtime
- In
middleware.ts, block unauthenticated traffic early and set security headers (Permissions-Policy,Content-Security-Policy). - For Edge functions calling third-party APIs, sign requests server-side and keep keys in encrypted edge config (Vercel Edge Config, Cloudflare Secrets).
- Rate-limit per tenant at the edge to stop abuse before it hits your origin.
Webhooks and callbacks
- When OpenAI/Anthropic call your webhook, validate the signature, replay attack window (
timestamp), and tenant context (embed in payload). - Store idempotency keys to avoid executing actions twice.
- Audit webhook receivers periodically-many breaches come from forgotten endpoints that accept unauthenticated traffic.
Third-party integrations
- Create separate API keys per tenant when possible (e.g., separate Slack apps).
- For shared keys, enforce tenant context via metadata or tagging so you can trace usage.
- Monitor upstream SLAs; when an external provider degrades, your agent might thrash and create cost spikes.
Operational security & monitoring
Secrets & API keys
- Store secrets in managed vaults (AWS Secrets Manager, Doppler, 1Password) and load them via environment variables in Next.js.
- Rotate on a schedule (monthly) or after incidents. Automate rotation via scripts/Bot workflows.
- Track secret usage by logging token IDs rather than raw values.
Logging architecture
- Log every request with
{ tenant_id, user_id, route, correlation_id, status, latency }. - For RAG: log chunk IDs returned, vector DB latency, filters applied.
- For agents: log tool invocations, arguments hash, MCP errors.
- Send logs to observability stacks (PostHog, Datadog, New Relic) with alerts for anomalies (cross-tenant attempts, repeated tool denials, fast token burn).
Monitoring dashboards
- Tenant health: usage, error rate, token spend, throttled requests.
- Security signals: failed auth, prompt injection detections, cross-tenant retrieval attempts.
- RAG performance: retrieval latency, missing citations, cache hit rate.
- Agent metrics: tool success/failure, longest-running actions, human escalations.
Incident response
- Detect - alert triggers or user report.
- Contain - disable affected feature, revoke keys, lock impacted tenants.
- Investigate - pull logs via correlation ID, replay the scenario, identify blast radius.
- Remediate - patch code/config, add tests.
- Review - post-incident writeup, update runbooks.
Practicing quarterly tabletop exercises ensures everyone knows their role.
Vendor & dependency evaluation
When selecting identity providers, vector databases, LLM APIs, or agent frameworks, ask:
- Do they support tenant namespaces or scoped API keys?
- What compliance reports can they share (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA)?
- How do they expose logs-and can you export them for SIEM ingestion?
- Can you enforce per-tenant rate limits or spend caps upstream?
- How quickly can credentials be rotated if compromised?
- Do they meet your data residency requirements?
Bake these questions into vendor security questionnaires to avoid migrations later.
Performance & cost trade-offs
- RLS overhead: Policies add predicates to every query. Mitigate with composite indexes, query caching, and careful connection pooling.
- Logging volume: Structured logs per tenant are necessary but pricey. Tier retention: hot logs (7-30 days) for Datadog/PostHog, cold storage (S3) for audits.
- Guardrails vs latency: Output filtering, reranking, and AI moderation add milliseconds. Decide which surfaces can afford the extra cost (admin tools yes, anonymous landing pages maybe no).
- Caching: Per-tenant caches reduce compute but complicate invalidation. Global caches are simpler but risk leakage.
- AI spend: Track token usage, reranker calls, and vector queries per tenant. Alert when a tenant burns 3× its normal spend to prevent shock invoices.
Share these trade-offs with finance/product so SLAs, pricing, and guardrails stay aligned.
Real-world incidents (sanitized)
- Missing RLS on new table: Finance team added
ledger_entrieswithout policies. Support staff saw multiple tenants’ data. Fix: enable RLS automatically in migrations, add CI checks that reject tables lacking policies, and expand integration tests. - Prompt injection via shared content: Customer uploaded docs instructing assistants to declare “everything is free.” Because ingestion wasn’t tenant-scoped, another tenant’s chatbot complied. Fix: namespace vector stores, sanitize ingestion, and add output filters that block cross-tenant mentions.
Use incidents like these to fuel chaos tests and regression suites so fixes don’t regress.
Control stack overview
Keep a living checklist across five tiers:
- Data layer - RLS, hybrid tenancy, backup strategy. Details in the multi-tenant SaaS architecture guide.
- Identity & auth - organization-aware identity, RBAC, feature gating, rate limiting.
- AI/RAG layer - prompt sanitization, RAG isolation, agent/tool RBAC. See the RAG architecture guide and LLM security guide.
- Observability - tenant-tagged logs, dashboards, anomaly alerts, cost attribution.
- Governance - access reviews, incident runbooks, vendor risk management, compliance evidence.
Document which controls are live, in progress, or planned; treat security like a product backlog.
Testing & validation
Platform-focused automated tests
- Tenant isolation suite: run queries as Tenant A and assert Tenant B data never appears (unit + integration tests).
- RAG regression tests: nightly job that runs fixed queries and checks expected chunk IDs + citations.
- Agent tool tests: simulate tool invocations with invalid roles, cross-tenant IDs, and injection payloads.
- Edge/API route tests: Playwright or Pact tests verifying headers, auth, and rate limiting.
Load & abuse testing
- Flood endpoints with high-volume requests to ensure rate limits and throttles behave correctly.
- Run chaos tests: drop the vector DB, spike latency, corrupt cache entries. The platform should degrade gracefully.
Manual penetration testing
- Cross-tenant RAG attacks, prompt injection variants, agent tool abuse, webhook tampering.
- Run before go-live, after major features, and at least twice a year for enterprise customers.
Penetration testing services include adversarial prompts, MCP abuse scenarios, and RLS validation tailored to your stack.
Security roadmap template
| Phase | Duration | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - Foundations | 2-4 weeks | Inventory tenants, add tenant_id, enable RLS, basic logging |
| 1 - Isolation hardening | 4-6 weeks | RBAC, org-aware identity, per-tenant rate limits, cache namespacing |
| 2 - AI guardrails | 4 weeks | Prompt sanitization, RAG validation, tool registry, monitoring |
| 3 - Observability & compliance | 3-5 weeks | Dashboards, anomaly alerts, access reviews, audit evidence |
| 4 - Resilience | Ongoing | Backup/PITR tests, chaos drills, vendor risk reviews |
Track this roadmap in Jira/Linear so security work ships alongside product features.
FAQ: AI Platform Security
What’s the most common security gap in AI platforms? Missing or improperly implemented row-level security (RLS). Application-level filters will eventually fail-database-level RLS is the essential last line of defense for multi-tenant data.
How much does an AI security audit cost? AI security assessments are scoped to the platform surface area, data sensitivity, and depth of testing. Pricing is quoted after a short intake so the scope, risk level, and evidence requirements are clear.
When should we implement AI security controls? Start with RLS and basic tenant isolation from day one. Add AI-specific guardrails (prompt injection defenses, RAG validation, agent RBAC) before shipping AI features to production. Comprehensive penetration testing should happen before enterprise launches and bi-annually thereafter.
What’s the difference between this guide and the LLM Security Guide? This guide covers platform architecture security (database, APIs, infrastructure, multi-tenancy). The LLM Security Guide focuses on model-level threats like prompt injection, OWASP Top 10 for LLMs, and input/output validation patterns. Use both together for comprehensive security.
Can we use this architecture with AWS/GCP instead of Vercel/Supabase? Yes. The security principles (RLS, tenant isolation, layered defenses) apply regardless of cloud provider. Implementation details differ (AWS RDS vs Supabase, Lambda vs Vercel Edge), but the threat model and control framework remain the same.
How do we handle security for RAG with third-party LLMs? Keep tenant context server-side, never send tenant IDs to third-party APIs in prompts. Use metadata filters before vector search, validate all retrieved chunks, and implement output filtering. See the RAG Architecture Guide for detailed patterns.
Conclusion & next steps
Platform security is a layered system spanning data, retrieval, agents, integrations, and operations. This guide provides the strategic framework-implementation requires careful customization for your architecture, compliance requirements, and risk tolerance.
Ready to secure your AI platform?
Option 1: AI Security Assessment
8-hour comprehensive security audit covering RLS implementation, RAG pipeline security, agent RBAC, and compliance readiness. Includes detailed report with prioritized remediation roadmap and risk scoring.
Fixed-fee after intake • Schedule assessment →
Option 2: Penetration Testing
Adversarial testing specifically designed for AI platforms: cross-tenant attacks, prompt injection variants, RAG poisoning, agent tool abuse, and MCP security. Includes automated scanning + manual red teaming.
Scoped per environment and risk level • View penetration testing →
Option 3: Security-First Platform Development
Build your AI platform with security baked in from day one: RLS schema design, RAG guardrails, agent RBAC, observability, and automated testing. Typical engagements run 8-16 weeks.
Contact for scoping • View platform development →
Option 4: Security Consulting Retainer
Ongoing security partnership: architecture reviews, security roadmap, incident response support, compliance preparation, and quarterly penetration testing.
Subscription-style retainer available after roadmap intake • Discuss retainer options →
Get the complete security implementation playbook
This guide covers strategic patterns and frameworks. The tactical implementation details-RLS policies, middleware code, guardrail implementations, testing harnesses, and monitoring dashboards-require customization for your specific stack, compliance requirements, and threat model.
Contact us to receive detailed implementation guidance, code examples, and runbooks tailored to your architecture.
Free resources:
- AI Platform Architecture Checklist - Complete security-first architecture scorecard
- AI Security Testing Checklist - Penetration testing preparation guide
Related resources:
- Multi-Tenant SaaS Architecture - Detailed RLS patterns and schema design
- RAG Architecture Guide - Hybrid search and retrieval security
- LLM Security Guide - Prompt injection and OWASP Top 10 for LLMs
- AI Agent Architecture - Agent orchestration and MCP integration





